Transfer Learning from a Clara Train Model using MONAI
Train a Spleen segmentation model using a pretrained segmentation model from NVIDIA GPU Cloud. The pretrained model is in Medical model archive (MMAR) format. We will create a new model in PyTorch model format (.pth) and then will convert the model to Torchscript (.ts) format using Tracing. Torchscript model is an intermediate representation of a PyTorch model that can then be run in a high-performance environment such as C++.
- Environment Setup
- Create Torchscript Model by Training a Pretrained MMAR Model
- Deploy the Torchscript Model as REST service using MIS
In this post, I will demonstrate how to train a spleen segmentation model starting with a pretrained model available in NVIDIA GPU cloud. In this demo MONAI official example is used as reference.
The end goal is to create a finefuned torchscript model. We will begin by instantiating a NVIDIA MMAR model and then we will finetune the model by refining the pretrained model weights.
Environment Setup
Install Monai Core on a Python 3.7 environment. I am using an Ubuntu 18.04 on an AWS grdnxlarge environment with 1 GPU.
Install Monai core and other packages
python -m pip install monai
Install 3 more packages nibabel, tqdm, lmdb
Create Torchscript Model by Training a Pretrained MMAR Model
Create a python script (.py) from the MONAI official notebook. You will find the python script here as well.
The script does following
- Download image dataset from http://medicaldecathlon.com/. Extract the downloaded images to a directory and create dataset path.
- Setup transforms for training and validation datasets. Create training and validation dataloaders.
- Fetch a pretrained model from NVIDIA Clara NGC
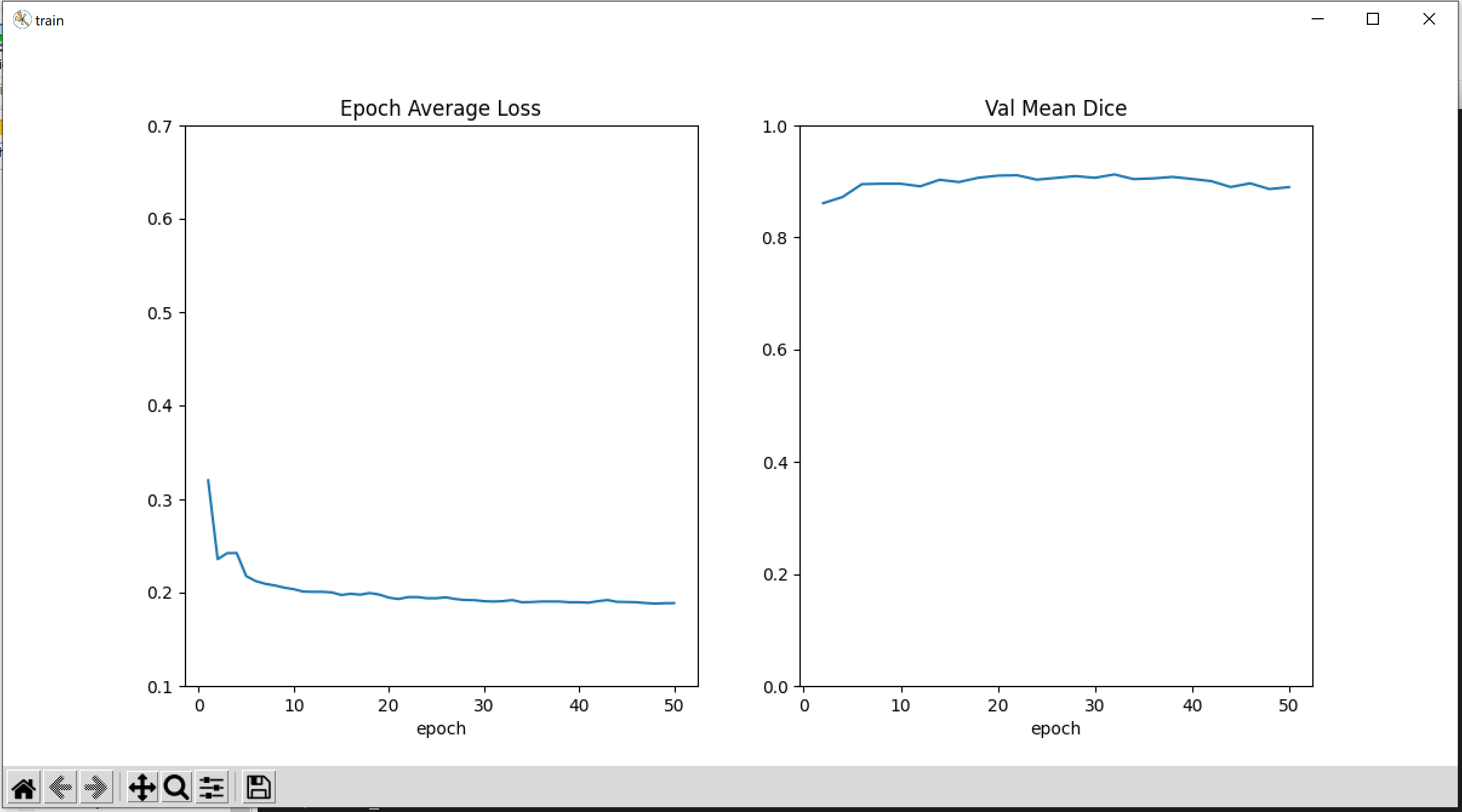
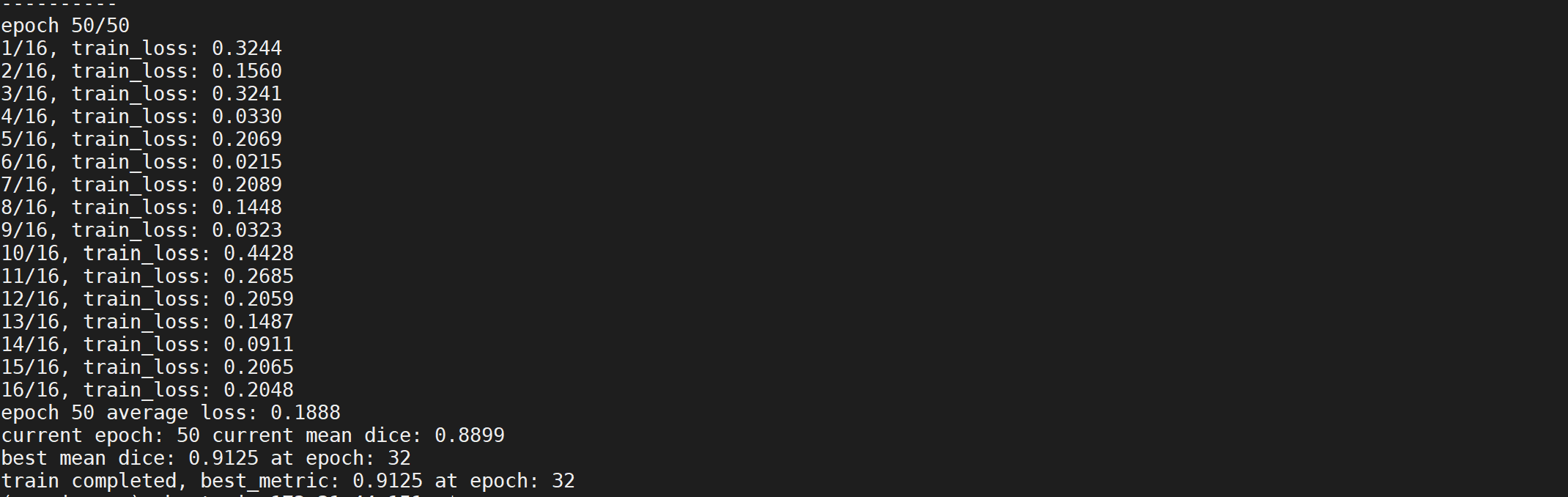
- Train the model with training data. Plot the loss and Dice metric
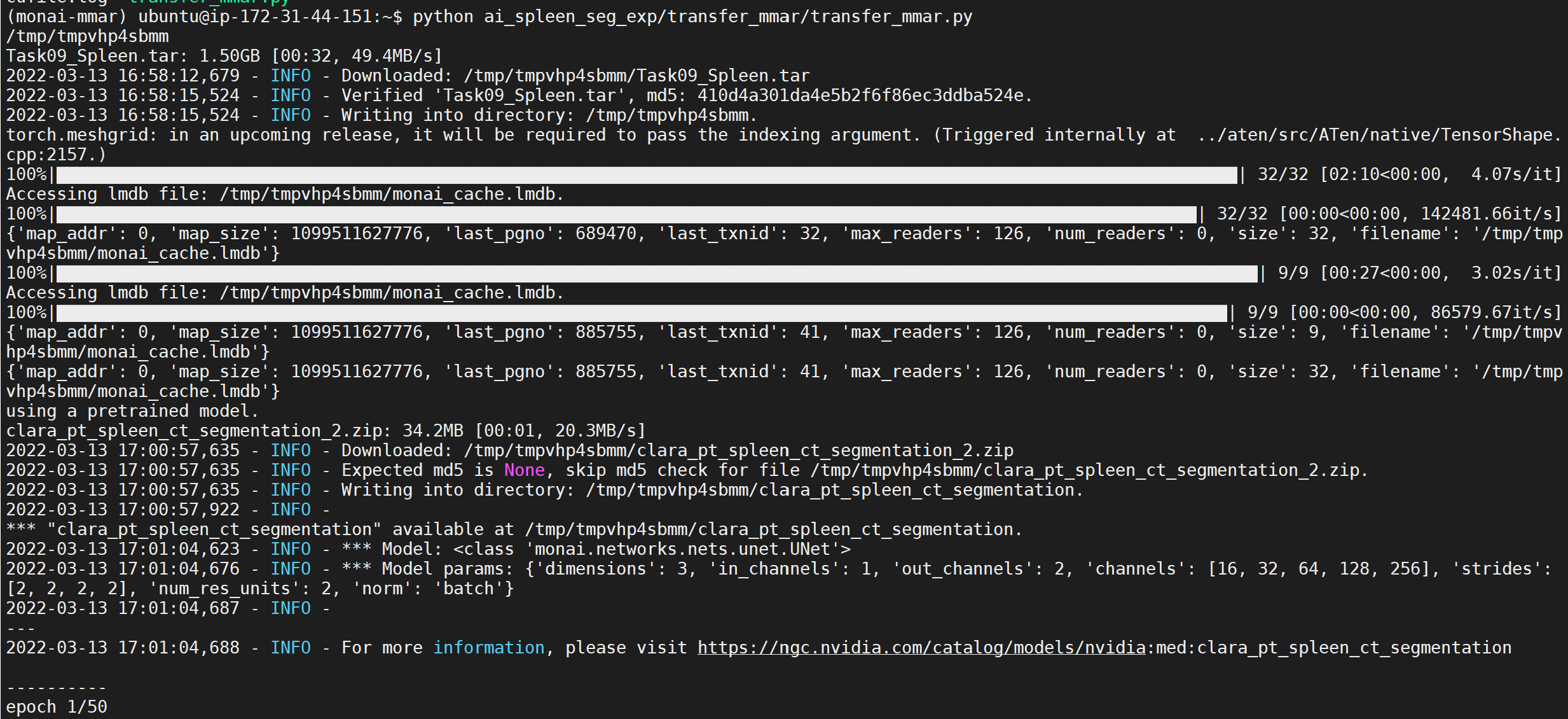
The script will generate two model representations; one in PyTorch and another in Torchscript. Models will be saved in the directory path set in MONAI_DATA_DIRECTORY environment variable. If no path is set models will be saved in /tmp.
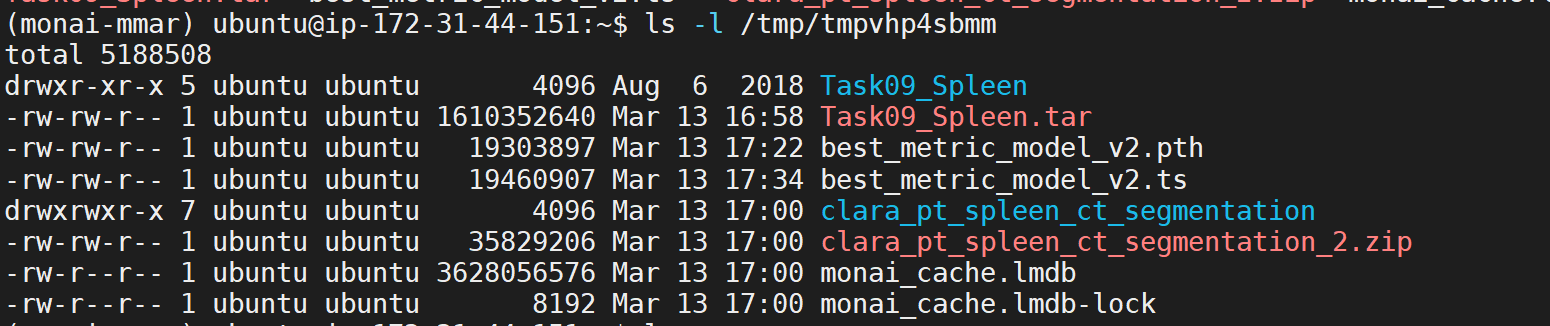
Convert PyTorch Model to Torchscript Model
In this example, Tracing is used to convert PyTorch model into Torchscript model. The process is described here in detail. A Torchscript model can be run in a high performance environment like C++ and is not dependent on python installation.
The loss and the segementation performance metrics Dice is shown in a plot.
Deploy the Torchscript Model as REST service using MIS
Steps to deploy the torchscript model (.ts) using MONAI Inference Service (MIS) is described in this post.